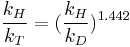Swain equation
The Swain equation relates the kinetic isotope effect for the proton/tritium combination with that of the proton/deuterium combination according to:
where kH,D,T are the reaction rate constants for the protonated, deuterated and tritiated reactants respectively.The Swain equation relates the kinetic isotope effect for the proton/tritium combination with that of the proton/deuterium combination according to: where kH,D,T is the reaction rate constant for the protonated, deuterated and tritiated reactants.
External links
References
- Use of Hydrogen Isotope Effects to Identify the Attacking Nucleophile in the Enolization of Ketones Catalyzed by Acetic Acid C. Gardner Swain, Edward C. Stivers, Joseph F. Reuwer, , Jr. Lawrence J. Schaad; J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1958; 80(21); 5885-5893. First Page